|
Open-CMSIS-Pack
Version 1.7.56
Delivery Mechanism for Software Packs
|
|
Open-CMSIS-Pack
Version 1.7.56
Delivery Mechanism for Software Packs
|
Configuration Wizard Annotations consist of annotation items and annotation modifiers. They create GUI-like elements in IDEs for configuration files (see Tool-specific display). Using a GUI-like approach makes it easier for the user to check and adapt configuration files to the application needs. The following rules apply:
+ in the table below can be followed by an identifier. When an identifier is present, the next code symbol following the symbol that matches the identifier is modified. See identifier example in the table. An identifier can not be used together with a skip-value.The following table lists the Configuration Wizard Annotations:
| Item | Text | Description |
|---|---|---|
| <h> | yes | Heading. Creates a header section. All items and options enclosed by <h> and </h> belong to one group and can be expanded. This entry makes no changes to code symbols. It is just used to group other items and modifiers. Excerpt from the Code Example // <h>Thread Configuration -- header without checkbox to group other items
// ...
// </h>
|
| <e>*+ | yes | Heading with enable. Creates a header section with a checkbox to enabled or disabled all items and options enclosed by <e> and </e>. Excerpt from the Code Example. // <e>Round-Robin Thread switching -- header with checkbox
// ===============================
//
// <i> Enables Round-Robin Thread switching. -- tooltip information for the header
#ifndef OS_ROBIN
#define OS_ROBIN 1 -- this value is set through the checkbox
#endif
// <o>Round-Robin Timeout [ticks] <1-1000>
// <i> Defines how long a thread will execute before a thread switch.
// <i> Default: 5
// <d> 5
#ifndef OS_ROBINTOUT
#define OS_ROBINTOUT 5
#endif
// </e>
<e>Round-Robin Thread switching ... </e> sets OS_ROBIN to 1 (checkbox enabled) or 0 (checkbox disabled) and encloses the OS_ROBINTOUT (Round-Robin Timeout) setting. See screen outcome in Tool-specific display. |
| <e.i>*+ | yes | Heading with Enable: modifies a specific bit (i) (example: <e.4> - changes bit 4 of a value). // <e.4>Serial Number
// <i>Enable Serial Number String.
// <i>If disabled, Serial Number String will not be assigned to USB Device.
#define USBD0_STR_DESC_SER_EN 1
|
| </h>, </e>, or </c> | yes | Heading, Enable, or Comment end. |
| <n> | yes | Notification text displayed // <n> This is shown as plain text
|
| <i> | yes | Tooltip help for previous item. // <i>This is shown as a tooltip when hovering over a text.
|
| <d> | yes | Default value for previous item. // <o MODE> Operation Mode
// <modeOne=> Mode 1
// <modeTwo=> Mode 2
// <d> modeOne
// #define MODE modeTwo
0 and 1 to signify "disabled" and "enabled", respectively. Annotating options with a default value enables tools to implement "reset to default" functionality. |
| <c>* | yes | Code enable: creates a checkbox to uncomment or comment code. All lines, including those with white spaces, get commented with double slashes (//) at the first found character when you disable the checkbox. // <c1> Comment sequence block until block end when disabled
//<i> This may carry the block's description
foo
+bar
-xFoo
// </c>
|
| <!c>* | yes | Code disable: creates a checkbox to comment or uncomment code. All lines, including those with white spaces, get commented with double slashes (//) at the first found character when you enable the checkbox. // <!c1> Comment sequence block until block end when enabled
//<i> This may carry the block's description
//
//foo
//
//+bar
//
//-xFoo
// </c>
|
| <q>*+ | yes | Option for bit values which can be set via a checkbox. // <h> Chip-select control
// <q> ASYNCWAIT: Wait signal during asynchronous transfer
// <i> Enables the FSMC to use the wait signal even during an asynchronous protocol.
// </h>
#define RTE_FSMC_BCR1_ASYNCWAIT 0 -- this is changed via a checkbox
|
| <o>*+ | yes | Option with selection or number entry. // <o>Round-Robin Timeout [ticks] <1-1000> -- text displayed on screen. Range of [ticks] is [1..1000]
// <i> Defines how long a thread will execute before a thread switch. -- tooltip info
// <i> Default: 5 -- tooltip info. Both displayed in one tooltip.
// <d> 5 -- default value
#ifndef OS_ROBINTOUT
#define OS_ROBINTOUT 5
#endif
// </e>
|
| <o.i>*+ | yes | Modify a single bit (example: <e.4> - modifies bit 4). // <o.4> <o.0>High-speed
// <i>Enable High-speed functionality (if device supports it).
#define USBD0_HS 0
|
| <o.x..y>*+ | yes | Modify a range of bits. (example: <o.4..5> - bit 4 to 5). // <h>String Settings
// <i>These settings are used to create the String Descriptor.
// <o.0..15>Language ID <0x0000-0xFCFF>
// <i>English (United States) = 0x0409.
// </h>
#define USBD0_STR_DESC_LANGID 0x0409
|
| <y>+ | yes | Enter a symbol or number. // <y>Value or Define Symbol that specifies number of open files <1-16>
// <i>Define number of files that can be opened at the same time.
#define FAT_MAX_OPEN_FILES maxFiles
// <y FAT_MAX_OPEN_FILES>Value or Define Symbol that specifies number of open files <1-16>
#define OTHER_SYMBOL "This is a text"
#define FAT_MAX_OPEN_FILES 8
|
| <s>*+ | yes | Option with ASCII string entry. // <s>Manufacturer String
// <i>String Descriptor describing Manufacturer.
#define USBD0_STR_DESC_MAN L"Keil Software"
|
| <s.i>*+ | yes | Option with ASCII string entry and a size limit of i characters. // <s.126>Manufacturer String
// <i>String Descriptor describing Manufacturer.
#define USBD0_STR_DESC_MAN L"Keil Software"
|
| <a.i>*+ | yes | Option for array entry and a size of i elements. // <a.16 PUBLIC_KEY> Public key for signing <0..255> <f.h>
// <d> {0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00}
#define PUBLIC_KEY {0x00, 0x01, 0x02, 0x03, 0x04, 0x05, 0x06, 0x07, 0x08, 0x09, 0x0A, 0x0B, 0x0C, 0x0D, 0x0E, 0x0F}
The example makes use of the value range modifier to constrain each array element to byte size, has a default value of all-zero, and uses the format specifier to ensure it is displayed as hexadecimal in the tool. GUI tools should support array lengths up to 64 elements. |
| skip example <qn>; <on>; <on.i>; <sn>; <sn.i> | n/a | Skip n items. Can be applied to all annotation items marked with a * in this table. // <o2>Skip 2 and modify the third item after this entry <1-9>
#define VALUE1 1000
#define VALUE2 2000
#define MODIFY_THIS 3000
|
| identifier example <q identifier> <e identifier> <o identifier> <s identifier> <y identifier> <e.i identifier> <o.i identifier> <s.i identifier> | n/a | Modify the item given by the identifier. Can be applied to all annotation items marked with a + in this table. // <o MODIFY_THIS>Modify the item after "MODIFY_THIS" <1-9>
#define VALUE1 1000
#define VALUE2 2000
#define MODIFY_THIS 3000
|
| Modifier | Description | |
| <0-31> | no | (deprecated1, see new range modifier below) Value range for option fields. Both endpoints are inclusive. |
| <0-100:10> | no | (deprecated1, see new range modifier below) Value range for option fields with step 10. Both endpoints are inclusive. |
| <0x40-0x1000:0x10> | no | (deprecated1, see new range modifier below) Value range in hex format and step 16. Both endpoints are inclusive. |
| <-32..31> | no | Value range for option fields supporting negative numbers. Both endpoints are inclusive. |
| <-50..100:10> | no | Value range for option fields with step 10 supporting negative numbers. Both endpoints are inclusive. |
| <-0x40..0x1000:0x10> | no | Value range in hex format and step 16 supporting negative numbers. Both endpoints are inclusive. |
| <value=> | yes | Creates a drop down-list and displays the text. value is written to the next item. Excerpt from the Code Example. // <o>Timer Thread Priority -- creates a drop-down with the list below.
// <1=> Low
// <2=> Below Normal <3=> Normal <4=> Above Normal
// <5=> High
// <6=> Realtime (highest)
// <i> Defines priority for Timer Thread -- tooltip info
// <i> Default: High -- tooltip info
// <d> 5 -- default value
#ifndef OS_TIMERPRIO
#define OS_TIMERPRIO 5
#endif
|
| <identifier=> | yes | Creates a drop down-list and displays the text following the definition of the identifiers dwt, systick and user. Note that this can only be used with options taking a key identifier (<o identifier>). The identifier corresponding to the selected text replaces the identifier following the key-identifier specified by the <o ...> tag. // <o TIMESTAMP_SRC>Time Stamp Source
// <dwt=> DWT Cycle Counter
// <systick=> SysTick
// <user=> User Timer
// <i>Selects source for 32-bit time stamp
#define TIMESTAMP_SRC dwt
In this example, the screen would show the option Time Stamp Source. The field value would display the text DWT Cycle Counter. TIMESTAMP_SRC is set to dwt. When clicking on the field, a drop-down would show all options. See Tool-specific display. Use case for an assignment of an enumeration to a variable: // <o redPortMode> Red port mode
// <OutPushPull_GPIO=> PushPull
// <OutOpenDrain_GPIO=> OpenDrain
// <i>Selects GPIO output
ledConf.redPortMode = OutOpenDrain_GPIO;
The example creates an option with the text Red port mode and a drop down-list showing the text items PushPull and OpenDrain. The corresponding identifier OutPushPull_GPIO or OutOpenDrain_GPIO will be used to replace the identifier after the key-identifier redPortMode. |
| <#+1> <#-1> <#*8> <#/3> | no | Modifies the entered or displayed value according to the operator (add, sub, mul, div). The changed value is set for the code symbol. Excerpt from Code Example. // <o>Default Thread stack size [bytes] <64-4096:8><#/4>
// <i> Defines default stack size for threads with osThreadDef stacksz = 0
// <i> Default: 200
#ifndef OS_STKSIZE
#define OS_STKSIZE 50
#endif
|
| <f.format-specifier> | no | Format specifier for graphical display of integer value. The format-specifier must be one of
// <o MY_DECIMAL_1> A decimal option <f.d>
#define MY_DECIMAL_1 13 -- displayed as decimal "13" in the tool
// <o MY_DECIMAL_2> Another decimal option <f.d>
#define MY_DECIMAL_2 0x10 -- displayed as decimal "16" in the tool
// <o MY_HEX> A hexadecimal option <f.h>
#define MY_HEX 52 -- displayed as hexadecimal "0x34" in the tool
|
1 Tools are expected to continue support of deprecated features but annotated files shall be updated to the new version.
You can copy the code into a C-file and check the outcome in the uVision Editor.
It is left to the development tool to interpret and display Configuration Wizard Annotations. The uVision IDE displays the code above in the following way:
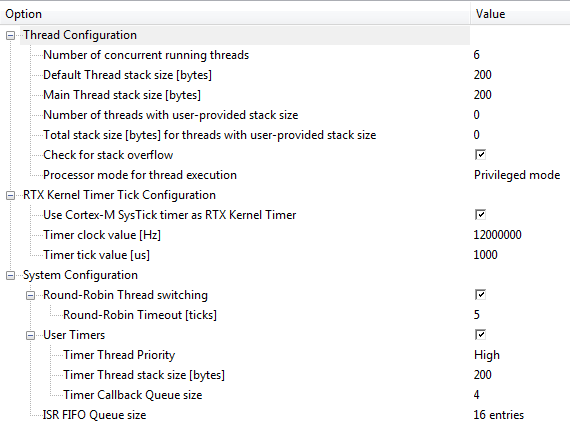
Where
Option are device properties, which can be represented in a tree structure. Each item can have an explanatory tooltip.
Value sets the option value. Can contain controls to encapsulate data in predefined drop-down lists.